2021年8月10日
Fire in Space
Image Credit: NASA
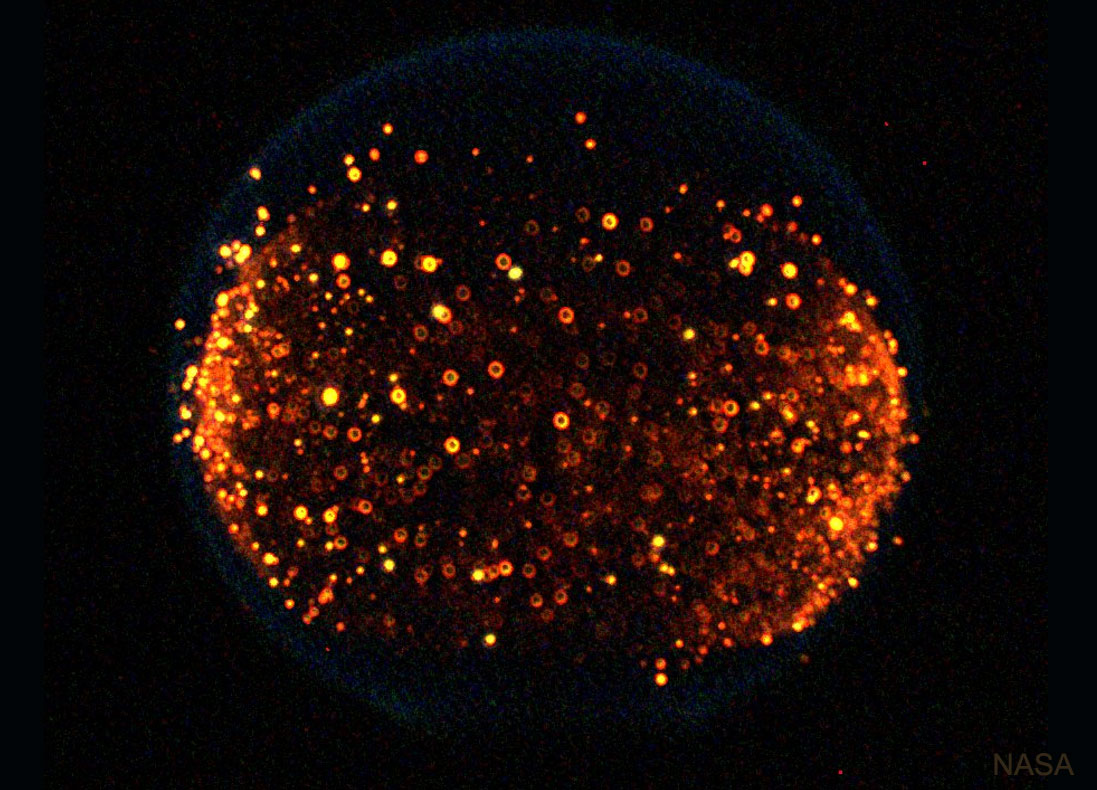
Explanation: What does fire look like in space? In the gravity on Earth, heated air rises and expands, causing flames to be teardrop shaped. In the microgravity of the air-filled International Space Station (ISS), however, flames are spheres. Fire is the rapid acquisition of oxygen, and space flames meet new oxygen molecules when they float by randomly from all directions — creating the enveloping sphere. In the featured image taken in the ISS’s Combustion Integration Rack, a spherical flame envelopes clusters of hot glowing soot. Without oxygen, say in the vacuum of empty space, a fire would go out immediately. The many chemical reactions involved with fire are complex, and testing them in microgravity is helping humanity not only to better understand fire — but how to put out fire, too.
Tomorrow’s picture: bubble cloud row
太空环境里的火
影像提供: NASA
说明: 太空的火长什么样子?在地球的重力环境里,受热的空气会上升膨胀,让火焰呈泪滴形。然而,在国际太空站(ISS)注满空气的微重力环境里,火焰呈球形。因为火是物质与氧快速结合的表现,而在太空中,氧分子从四面八方随机飞来,造就了太空火焰球形的外包。于这幅摄于国际太空站.整合式燃烧架内的主题影像里,火焰球状的外包之内,还可见到成群的明亮炽热烟灰。不过,在像真空这些无氧的环境里,火会立即熄灭。与火有关的许多化学反应极为复杂,在微重力环境里进行测试,可让人类对火有更深入的了解,也知道该如何灭火。
明日的图片: bubble cloud row